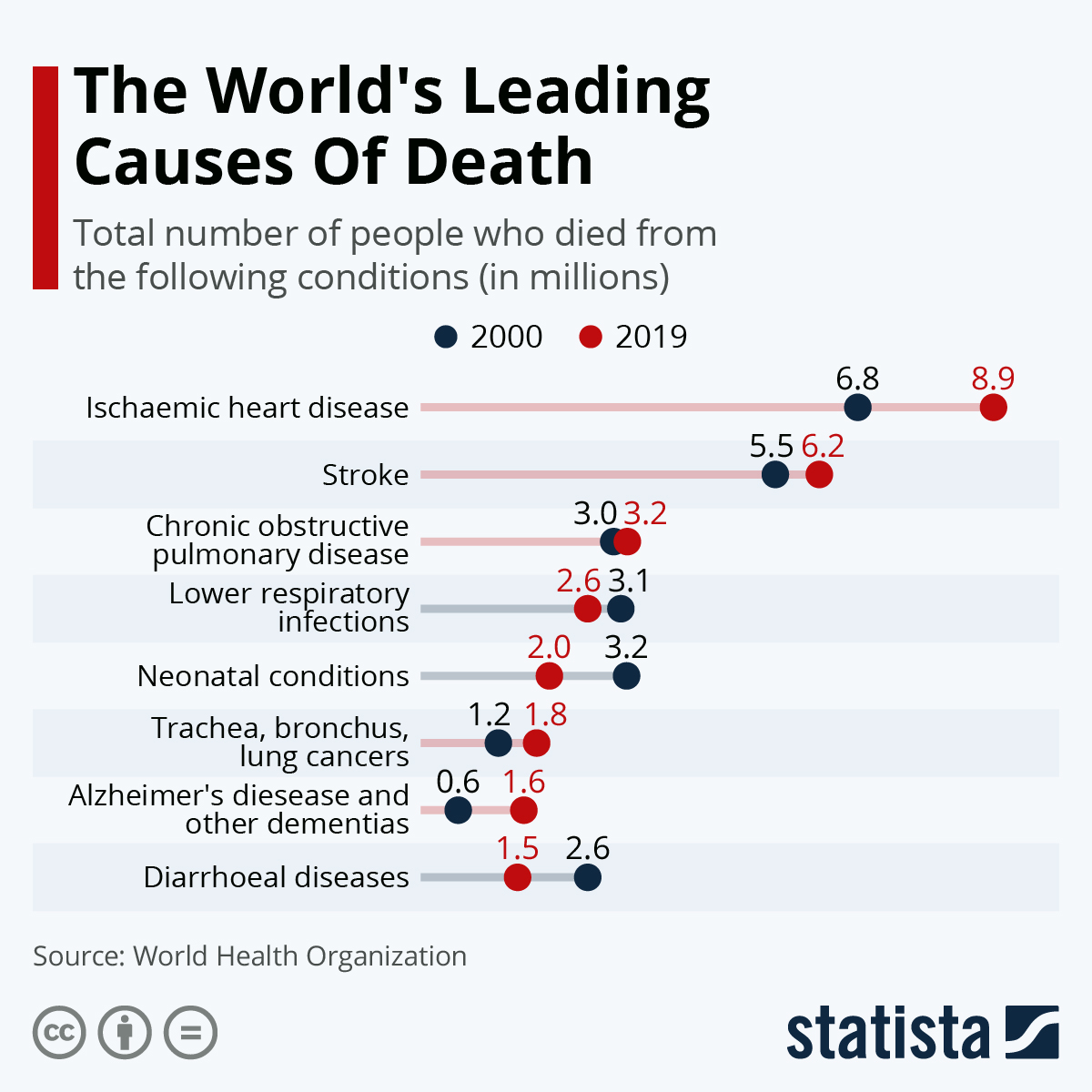
New World Health Organization data has detailed the leading caused of death worldwide in 2019. Collectively the top 10 causes of death accounted for 55 percent of the 55.4 million deaths that were on record last year with seven of them noncommunicable diseases. The top causes globally, in order of lives lost, are associated with three broad conditions - cardiovascular (ischaemic heart disease, stroke), respiratory (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lower respiratory infections) and neonatal conditions (birth asphyxia and birth trauma, neonatal sepsis and infections, as well as preterm birth complications).
Back in 2000, Ischaemic heart disease was the leading cause of death and it remains the top killed today, accounting for 8.9 million deaths in 2019 or 16 percent of total deaths worldwide. Strokes comes second on the list, responsible for 11 percent of all deaths or 6.2 million people. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease comes third on the list of the deadliest conditions, associated with 3.2 million deaths in 2019. While the number of deaths from Ischaemic heart disease and strokes increased noticeably between 2000 and 2019, the death toll from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease only grew slightly.
Despite the grim contents of the WHO's data, there were some positive developments. HIV/AIDS dropped from being the eighth leading cause of death in 2000 to the 19th leading cause of death in 2019 amid improved diagnosis speeds and treatments. Likewise, tuberculosis dropped from seventh place to 13th between 2000 and 2019 amid a 30 percent fall in deaths.